Table of Contents
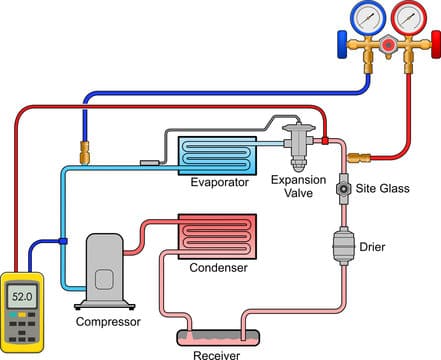
Refrigerators are devices that work 24 hours a day and night to perform cooling functions. Modern refrigeration systems depend on the refrigeration cycle, necessary for effective temperature management in various applications. This cycle, which often appears in a refrigeration cycle diagram, shows how refrigerant is transformed and moved through various components to provide effective heating and cooling. A variety of essential processes and components are involved in the basic refrigeration cycle, and they all function together in transferring heat from one area to another.
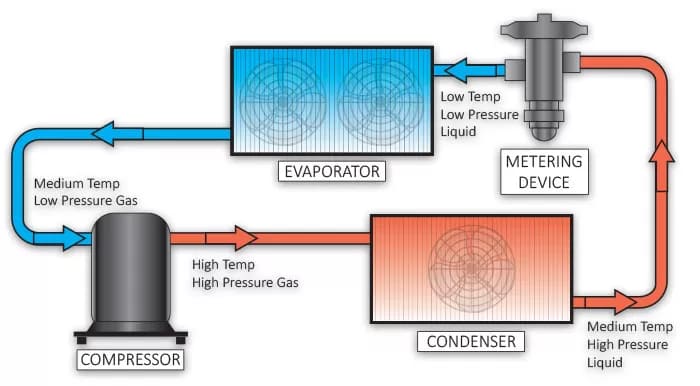
These processes are represented visually in a refrigeration cycle diagram, showing how the refrigerant moves and changes state as it passes through the system. The compressor, condenser, metering device, and evaporator are the four main parts of the basic refrigeration cycle diagram, and they are all connected in a circle. This simple diagram helps us understand how the refrigerant changes through the cycle.
Components of the Refrigeration Cycle
The compressor, condenser, metering device, and evaporator are the four main parts of the basic refrigeration cycle diagram, and they are all connected in a circle.
Compressor
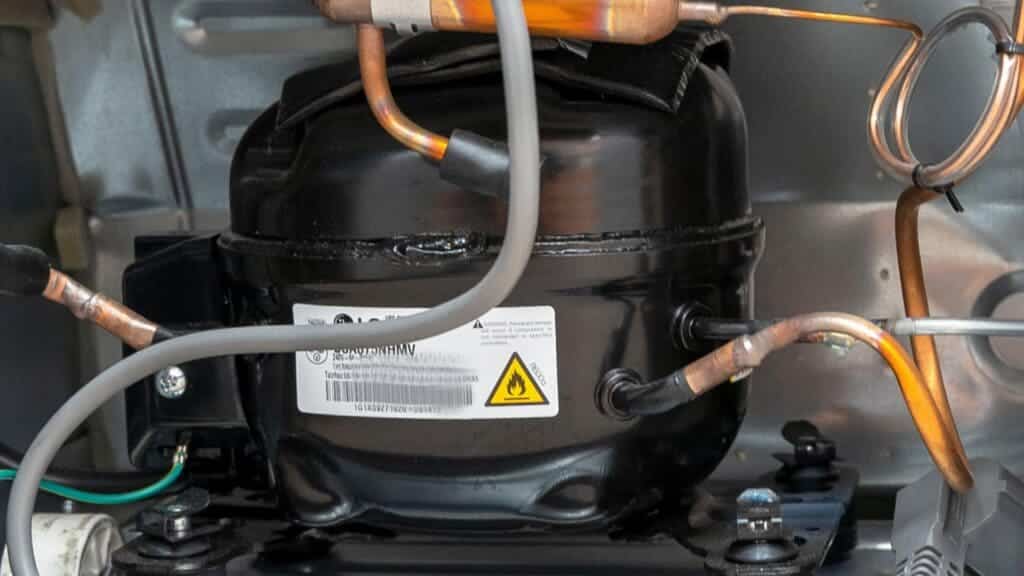

The compressor compresses the refrigerant vapor to begin the cycle. This process increases the refrigerant’s pressure and temperature, making it a high-pressure, high-temperature gas. When it leaves the compressor, the refrigerant continues to the cycle’s next phase.
Condenser Coil
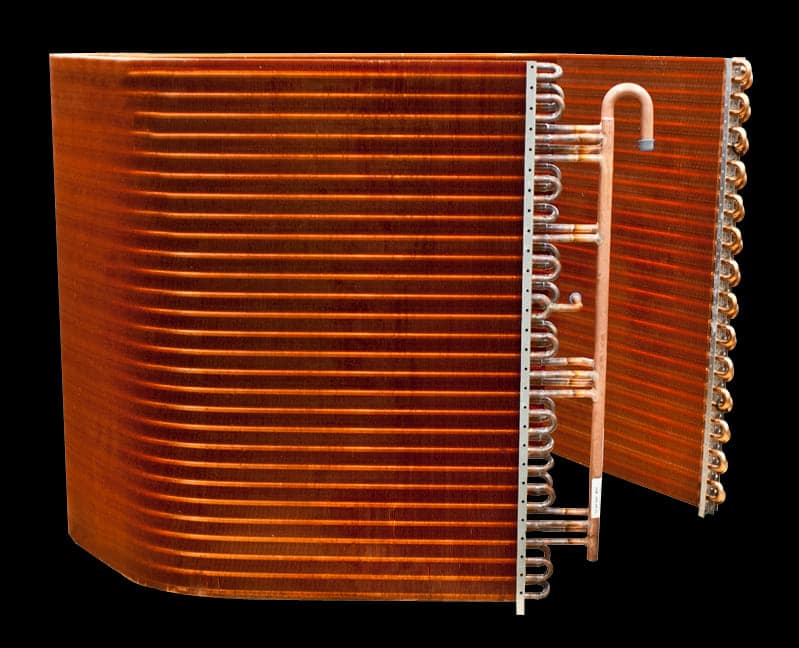
The refrigeration cycle diagram shows that the gas enters the condenser coil at a high temperature and pressure. In this situation, the refrigerant cools the surrounding air and transforms it into a high-pressure liquid by releasing heat. This essential stage in the process, known as heat transfer, allows the refrigerant to dissipate the heat from the cooled area.
Metering Device
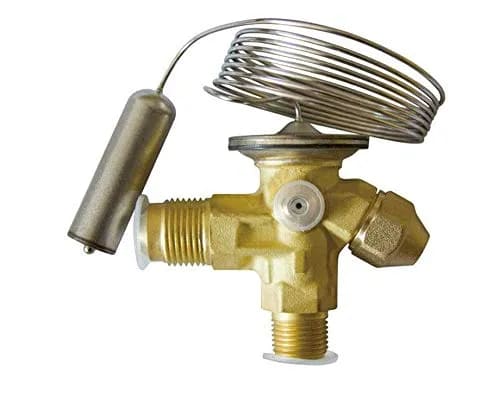

After exiting the condenser, the refrigerant travels through a metering device. By controlling the flow of liquid refrigerant into the evaporator, this device reduces the pressure inside the evaporator and causes it to expand. This expansion significantly cools the refrigerant, preparing it for the heat absorption phase.
Evaporator
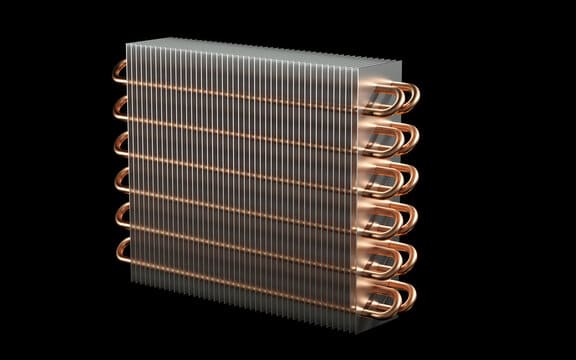
The evaporator’s low-pressure, cold liquid refrigerant absorbs the heat from the air or material being cooled. As a result of this absorption, the refrigerant re-evaporates into a low-pressure vapor and goes back to the compressor to start the refrigeration cycle again.
Any refrigerator must have effective cooling, and the evaporator is critical to this process. Optimizing cooling efficiency can reduce energy expenses and extend the life of your appliance. To get the highest performance possible, select the best refrigerator evaporator.
Reversing valve
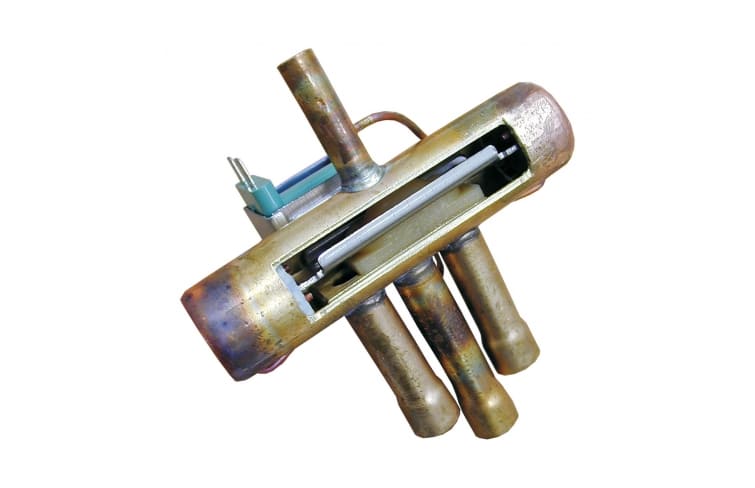

The cycle in a heat pump refrigeration cycle diagram has additional components, such as a reversing valve. The reversing valve allows the system to switch between the heating and cooling phases. When the system is in heating mode, the evaporator and condenser work in reverse, enabling the heat to be taken from the outside air and released into the interior, heating it.
Refrigerant

A refrigerant is a substance used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. These systems cool air or items by absorbing heat and transmitting it in a cycle. Different types of refrigerants have unique physical and chemical characteristics.
Modes of Refrigeration Cycle
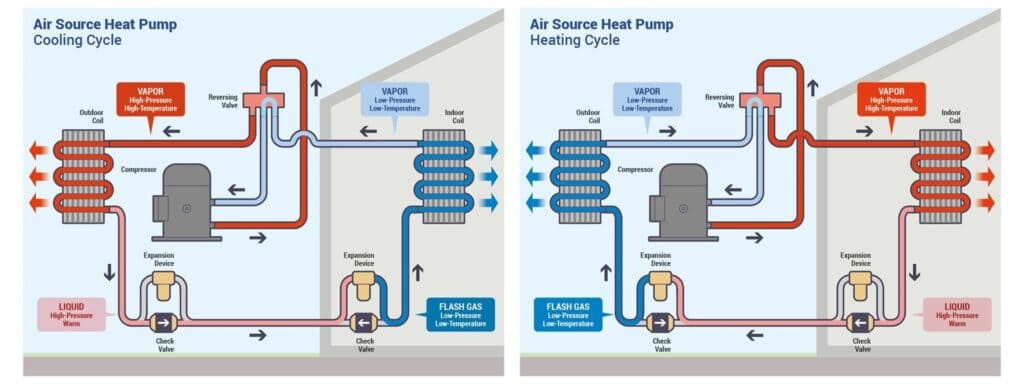
The refrigeration cycle moves heat from one place to another, efficiently heating or cooling an area as required. The refrigerant’s ability to transition between a liquid and a vapor and back again, collecting and releasing heat, allows this heat transfer process.
Cooling Mode
Activating the cooling mode causes the evaporator to absorb heat from the indoor air, which makes the refrigerant vaporize at low pressure. The system then circulates the cooled air around the room, lowering the temperature. The refrigerant, now a vapor, returns to the compressor to begin the cycle again.
Heating Mode
The cycle runs in reverse during heating mode, which is made possible by the reversing valve. Even in cold temperatures, the evaporator transforms into the condenser and takes up heat from the surrounding air.
Now carrying the absorbed heat, the refrigerant is compressed and circulated, releasing the heat and warming the interior
Key Processes in the Refrigeration Cycle
A simple refrigeration cycle diagram consists of four main processes. The refrigeration cycle components use these critical processes to accomplish the refrigeration cycle.
Compression
This essential step increases the refrigerant’s temperature and pressure and prepares it for heat dissipation. Refrigerant gas at high pressure is necessary for the condenser’s efficient heat exchange.
Condensation
Generally, through condenser coils, the high-pressure gas in the condenser loses its heat to the surrounding air. This process changes The refrigerant into a high-pressure liquid, making it suitable for expansion.
Expansion
The metering device controls the flow of refrigerant, allowing it to expand and drop in pressure. The evaporator requires this low-pressure liquid to absorb heat,
Evaporation
Heat-absorbing refrigerant turns into a low-pressure vapor in the evaporator. Air conditioning and refrigeration systems’ primary purpose is to cool the surrounding air or materials through heat absorption.
Practical Applications

The refrigeration cycle is a versatile process with multiple applications in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. From commercial refrigeration and household air conditioning to freezing and industrial process cooling, efficient heat transfer is essential to contemporary living.
- Air conditioning and refrigeration systems use the refrigerant cycle diagram to control indoor temperatures and maintain perishable items.
- By efficiently cooling the air, the residential and commercial air conditioning cycle maintains pleasant indoor temperatures.
- The cycle in industrial refrigeration keeps the temperature low enough to store sensitive goods like food and medications.
- Heat pumps effectively operate in various climates, providing both heating and cooling.
- Automotive air conditioning systems use the refrigeration cycle to create a comfortable driving environment.
- Cryogenic applications use advanced refrigeration cycle forms to achieve extremely low temperatures required for preserving biological samples, conducting scientific research, and producing industrial gases.
- Heat pumps are flexible and affordable options for year-round climate management because they can reverse the cycle, taking heat from the air, earth, or water and transferring it within.
Conclusion
Ultimately, it is crucial to understand the components and functions of the refrigeration cycle of refrigerators and air conditioning systems. The refrigeration cycle diagram explains the process, which shows how the refrigerant flows through the system, changing states and transferring heat. The key components, such as the compressor, condenser coil, metering device, and evaporator, work together for the proper functioning of the devices.
The refrigeration cycle effectively manages temperature by switching between the heating and cooling modes through its dual functionality and using critical processes of compression, condensation, evaporation, and expansion. This basic refrigeration cycle is crucial in temperature regulation techniques and is equally essential in residential and commercial sectors. From commercial refrigeration and household air conditioning to freezing and industrial process cooling, the importance of this cycle is undeniable. From commercial refrigeration and household air conditioning to freezing and industrial process cooling, efficient heat transfer is essential to contemporary living.